Примеры преобразования двоичного кода в Ascii
Входные данные
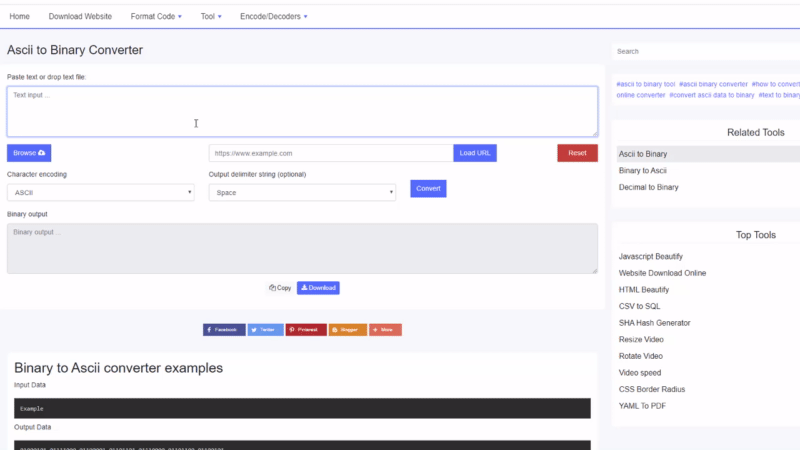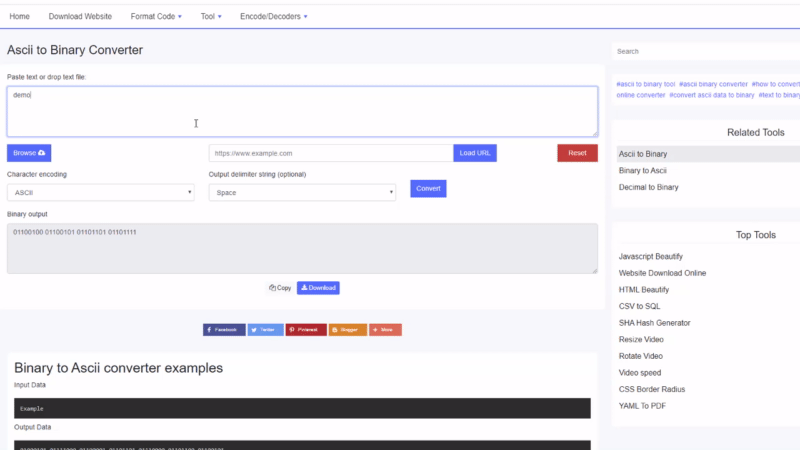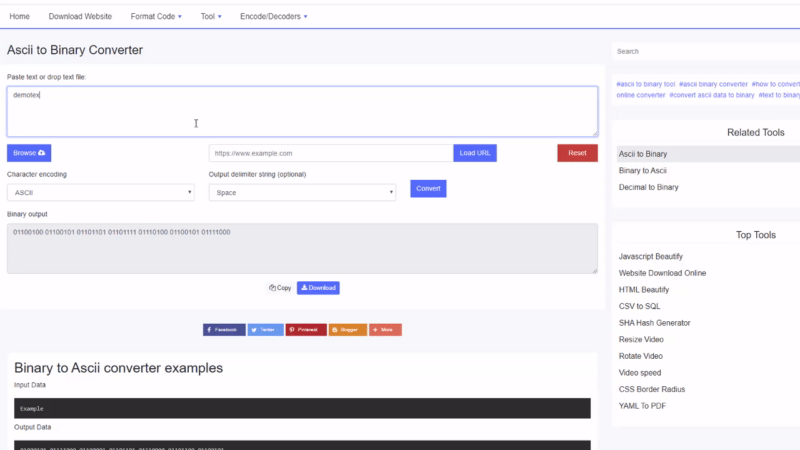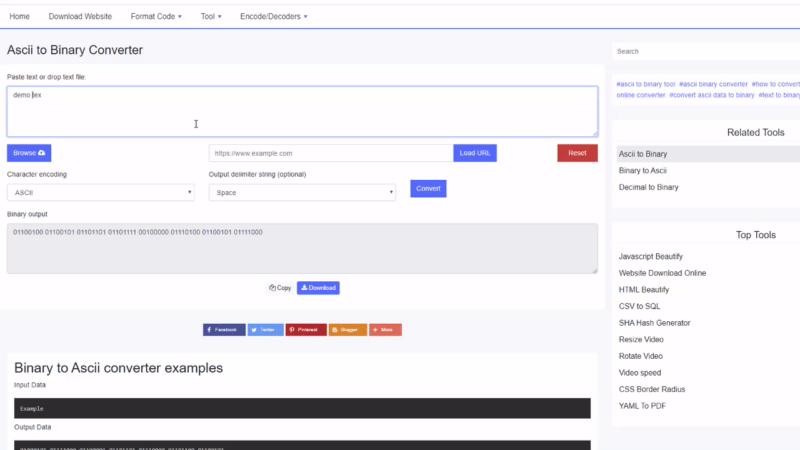
ExampleВыходные данные
01000101 01111000 01100001 01101101 01110000 01101100 01100101Как преобразовать двоичный файл в текст
Преобразование текста в двоичный код ASCII:
- Получить персонаж
- Получить десятичный код символа из таблицы ASCII
- Преобразовать десятичный байт в двоичный
- Продолжить со следующим символом
Как преобразовать двоичный код 01000001 в текст?
Используйте таблицу ASCII:
«П» => 80 = 26+24 = 010100002
"л" => 108 = 26+25+23+22 = 011011002
"а" => 97 = 26+25+20 = 011000012
«А» = 6510 = 64+1 = 26+20 = 010000012
«0» = 4810 = 32+16 = 25+24 = 00110000
Таблица преобразования двоичного текста в текст ASCII
| шестнадцатеричный | Бинарный | ASCII-символ |
|---|---|---|
| 00 | 00000000 | НУЛ |
| 01 | 00000001 | СОХ |
| 02 | 00000010 | СТХ |
| 03 | 00000011 | ЕТХ |
| 04 | 00000100 | EOT |
| 05 | 00000101 | ENQ |
| 06 | 00000110 | ПОДТВЕРЖДЕНИЕ |
| 07 | 00000111 | БЕЛ |
| 08 | 00001000 | БС |
| 09 | 00001001 | ХТ |
| 0А | 00001010 | НЧ |
| 0В | 00001011 | ВТ |
| 0С | 00001100 | ФФ |
| 0D | 00001101 | CR |
| 0Э | 00001110 | ТАК |
| 0F | 00001111 | СИ |
| 10 | 00010000 | ДЛЭ |
| 11 | 00010001 | DC1 |
| 12 | 00010010 | DC2 |
| 13 | 00010011 | DC3 |
| 14 | 00010100 | DC4 |
| 15 | 00010101 | НАК |
| 16 | 00010110 | СИН |
| 17 | 00010111 | ЭТБ |
| 18 | 00011000 | МОЖЕТ |
| 19 | 00011001 | ЭМ |
| 1А | 00011010 | SUB |
| 1Б | 00011011 | ESC |
| 1С | 00011100 | ФС |
| 1D | 00011101 | GS |
| 1Э | 00011110 | РС |
| 1эт | 00011111 | НАС |
| 20 | 00100000 | Космос |
| 21 | 00100001 | ! |
| 22 | 00100010 | " |
| 23 | 00100011 | # |
| 24 | 00100100 | $ |
| 25 | 00100101 | % |
| 26 | 00100110 | & |
| 27 | 00100111 | ' |
| 28 | 00101000 | ( |
| 29 | 00101001 | ) |
| 2А | 00101010 | * |
| 2Б | 00101011 | + |
| 2С | 00101100 | , |
| 2D | 00101101 | - |
| 2Э | 00101110 | . |
| 2F | 00101111 | / |
| 30 | 00110000 | 0 |
| 31 | 00110001 | 1 |
| 32 | 00110010 | 2 |
| 33 | 00110011 | 3 |
| 34 | 00110100 | 4 |
| 35 | 00110101 | 5 |
| 36 | 00110110 | 6 |
| 37 | 00110111 | 7 |
| 38 | 00111000 | 8 |
| 39 | 00111001 | 9 |
| 3А | 00111010 | : |
| 3Б | 00111011 | ; |
| 3С | 00111100 | < |
| 3D | 00111101 | "=" |
| 3Э | 00111110 | > |
| 3F | 00111111 | ? |
| 40 | 01000000 | @ |
| 41 | 01000001 | А |
| 42 | 01000010 | Б |
| 43 | 01000011 | С |
| 44 | 01000100 | Д |
| 45 | 01000101 | Е |
| 46 | 01000110 | Ф |
| 47 | 01000111 | г |
| 48 | 01001000 | ЧАС |
| 49 | 01001001 | я |
| 4А | 01001010 | Дж |
| 4Б | 01001011 | К |
| 4С | 01001100 | л |
| 4D | 01001101 | М |
| 4Э | 01001110 | Н |
| 4F | 01001111 | О |
| 50 | 01010000 | п |
| 51 | 01010001 | Вопрос |
| 52 | 01010010 | р |
| 53 | 01010011 | С |
| 54 | 01010100 | Т |
| 55 | 01010101 | U |
| 56 | 01010110 | В |
| 57 | 01010111 | Вт |
| 58 | 01011000 | Икс |
| 59 | 01011001 | Д |
| 5А | 01011010 | Z |
| 5Б | 01011011 | [ |
| 5С | 01011100 | \ |
| 5D | 01011101 | ] |
| 5Э | 01011110 | ^ |
| 5эт | 01011111 | _ |
| 60 | 01100000 | ` |
| 61 | 01100001 | а |
| 62 | 01100010 | б |
| 63 | 01100011 | с |
| 64 | 01100100 | г |
| 65 | 01100101 | е |
| 66 | 01100110 | ф |
| 67 | 01100111 | г |
| 68 | 01101000 | час |
| 69 | 01101001 | я |
| 6А | 01101010 | Дж |
| 6Б | 01101011 | к |
| 6С | 01101100 | л |
| 6D | 01101101 | м |
| 6Э | 01101110 | н |
| 6F | 01101111 | о |
| 70 | 01110000 | п |
| 71 | 01110001 | д |
| 72 | 01110010 | р |
| 73 | 01110011 | с |
| 74 | 01110100 | т |
| 75 | 01110101 | ты |
| 76 | 01110110 | в |
| 77 | 01110111 | ж |
| 78 | 01111000 | Икс |
| 79 | 01111001 | у |
| 7А | 01111010 | г |
| 7Б | 01111011 | { |
| 7С | 01111100 | | |
| 7D | 01111101 | } |
| 7Э | 01111110 | ~ |
| 7F | 01111111 | ДЕЛ |
Бинарная система
В двоичной системе счисления в качестве основы (основания) используется число 2. Как система счисления с основанием 2, она состоит только из двух чисел: 0 и 1.
Хотя она применялась в Древнем Египте, Китае и Индии для различных целей, двоичная система стала языком электроники и компьютеров в современном мире. Это наиболее эффективная система для обнаружения выключенного (0) и включенного (1) состояния электрического сигнала. Это также основа для двоичного кода, который используется для составления данных в компьютерных машинах. Даже цифровой текст, который вы сейчас читаете, состоит из двоичных чисел.
ASCII-текст
ASCII (американский стандартный код для обмена информацией) является одним из наиболее распространенных стандартов кодирования символов. Первоначально разработанный из телеграфных кодов, ASCII теперь широко используется в электронной связи для передачи текста.
Оригинальный ASCII основан на 128 символах. Это 26 букв английского алфавита (как в нижнем, так и в верхнем регистре); цифры от 0 до 9; и различные знаки препинания. В коде ASCII каждому из этих символов присваивается десятичное число от 0 до 127. Например, ASCII-представление заглавной буквы A равно 65, а строчной буквы a — 97.